Linux: Networking Commands Tutorial
This page shows the most frequently used linux networking commands.
Find Physical Address of Network Adapter (MAC Address)
Type ip link show or ifconfig -a
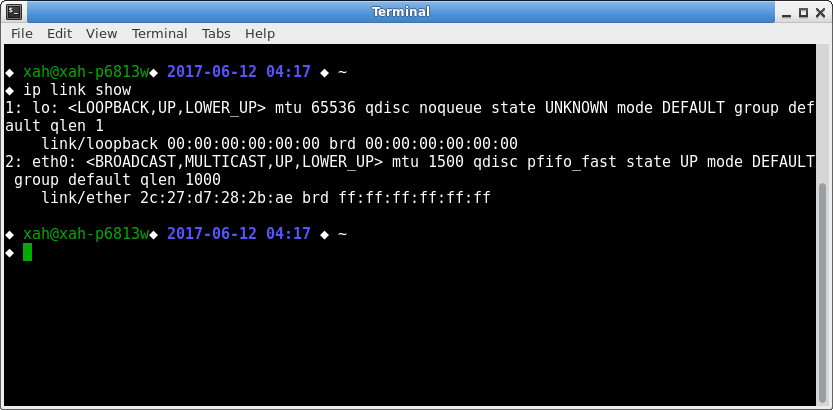
ip link show output
The eth0 is the network adapter.
The 2c:27:d7:28:2b:ae is its MAC address.
The lo one is software-based local loopback MAC address.
It is not a physical network adapter.
Find IP Address of Network Adapter
Type ip addr or ifconfig -a
For each adapter, its IPv4 address is shown in the line “inet”, and IPv6 address is shown in “inet6”.
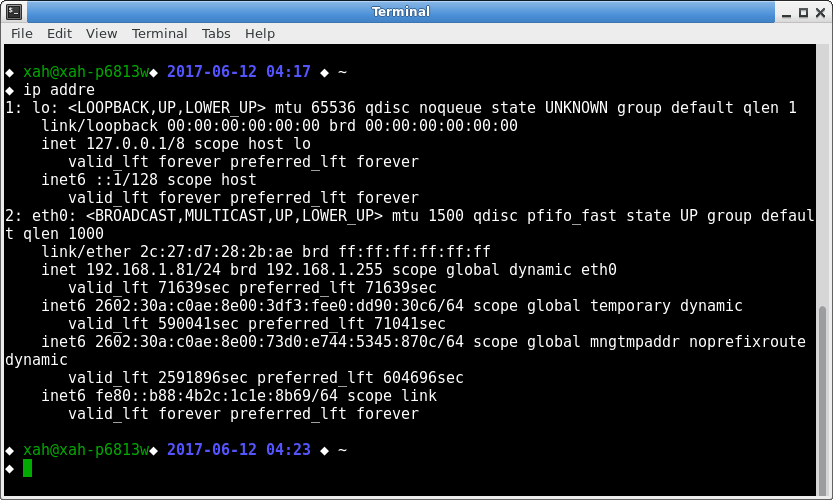
ip addre output
The eth0 is your network adapter.
The 192.168.1.81 is its current IPv4 address.
Find IP Address of Router
Type ip route. The line “default via” contains your router's IP address.
◆ ip route default via 10.0.2.2 dev eth0 proto static 10.0.2.0/24 dev eth0 proto kernel scope link src 10.0.2.15 metric 1 169.254.0.0/16 dev eth0 scope link metric 1000
Or, type route. The line “default” and the IP in column “Gateway” shows the IP address of router.
Find MAC Address of Router
First, find out your router's IP address. Then, type arp -a.
Sample output:
Address HWtype HWaddress Flags Mask Iface 10.0.2.2 ether 52:54:00:12:35:02 C eth0
Show Routing Table
Type ip route or route. Sample output:
◆ route Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface default 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0 link-local * 255.255.0.0 U 1000 0 0 eth0 192.168.1.0 * 255.255.255.0 U 1 0 0 eth0
◆ ip route default via 192.168.1.1 dev eth0 proto static 169.254.0.0/16 dev eth0 scope link metric 1000 192.168.1.0/24 dev eth0 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.1.3 metric 1
How to turn off my network interface?
ifconfig etho0 down→ turns network interface named etho0 off.ifconfig etho0 up→ turns network interface named etho0 on.
How to set IP address?
ifconfig etho0 192.168.1.86→ set IP address on network interface “etho0”.
How to set netmask?
ifconfig netmask 255.255.255.0→ set netmask of network interface “etho0”.
Using modern ip Command (iproute2)
iproute2 is a collection of utilities for controlling TCP and UDP IP networking and traffic control in Linux, in both IPv4 and IPv6 networks.
iproute2 is intended to replace an entire suite of standard Unix networking tools (often called “net-tools”) that were previously used for the tasks of configuring network interfaces, routing tables, and managing the ARP table.
iproute2 unifies the syntax for these various commands, which evolved over many years of Unix development.
Tools replaced by iproute2 are:
| purpose | legacy commands | iproute2 commands |
|---|---|---|
| Address and link configuration | ifconfig | ip addr, ip link |
| Routing tables | route | ip route |
| Neighbors | arp | ip neigh |
| VLAN | vconfig | ip link |
| Tunnels | iptunnel | ip tunnel |
| Multicast | ipmaddr | ip maddr |
| Statistics | netstat | ss |
General Syntax of ip command
the general syntax is this:
ip object command
, where the object is one of:
linkaddraddrlabelrouteruleneightunnelmaddrmroute
each object will accept different commands. To see what commands are available, type help after the object. For example, ip link help
How to find out if a network adapter is on or off?
ip link show. If it's on, it'll show “state UP”.
If it's off, it'll show “state DOWN”.
How to turn on/off a network adapter?
to turn on, type sudo ip link name up. Use “down” for off.
classic commands
ifconfig
ifconfig (interface configuration). for configure, control, and query TCP/IP network interface parameters
Common uses for ifconfig include setting an interface's IP address and netmask, and disabling or enabling a given interface
- to show active Network Interface, type
ifconfig - to show all Network Interface, type
ifconfig -a - to turn off a Network Interface, type
sudo ifconfig name down, where the name is typically “eth0” or “wlan0”. But for wireless network adapter, it may turn on itself after you turn it off. - to turn on a Network Interface, type
sudo ifconfig name up
Sample output:
◆ ifconfig -a
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 08:00:27:76:bb:55
inet addr:10.0.2.15 Bcast:10.0.2.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::a00:27ff:fe76:bb55/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:39 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:125 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:5433 (5.4 KB) TX bytes:15303 (15.3 KB)
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:16436 Metric:1
RX packets:44 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:44 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:3268 (3.2 KB) TX bytes:3268 (3.2 KB)
ping
used to test the reachability of a host on an Internet Protocol (IP) network and to measure the round-trip time for messages sent from the originating host to a destination computer.
Ping operates by sending Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo request packets to the target host and waiting for an ICMP response. In the process it measures the time from transmission to reception (round-trip time) and records any packet loss. The results of the test are printed in the form of a statistical summary of the response packets received, including the minimum, maximum, and the mean round-trip times, and sometimes the standard deviation of the mean.
ping, ping6
traceroute, tracepath
traceroute is a computer network diagnostic tool for displaying the route (path) and measuring transit delays of packets across an Internet Protocol (IP) network.
Traceroute sends a sequence of Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo request packets addressed to a destination host. Determining the intermediate routers traversed involves adjusting the time-to-live (TTL), aka hop limit, Internet Protocol parameter. Frequently starting with a value like 128 (Windows) or 64 (Linux), routers decrement this and discard a packet when the TTL value has reached zero, returning the ICMP error message ICMP Time Exceeded.
Traceroute works by increasing the TTL value of each successive set of packets sent. The first set of packets sent have a hop limit value of 1, expecting that they are not forwarded by the first router. The next set have a hop limit value of 2, so that the second router will send the error reply. This continues until the destination host receives the packets and returns an ICMP Echo Reply message.
Traceroute uses the returned ICMP messages to produce a list of routers that the packets have traversed. The timestamp values returned for each router along the path are the delay (aka latency) values, typically measured in milliseconds for each packet.
on Linux, by default, tracepath and tracepath6 is installed.
the traditional command traceroute requires superuser privilege. tracepath doesn't, and has fewer options.
netstat
netstat. Displays protocol statistics and current TCP/IP network connections.
netstat (network statistics) displays network connections (both incoming and outgoing), routing tables, and a number of network interface (network interface controller or software-defined network interface) and network protocol statistics.
It is used for finding problems in the network and to determine the amount of traffic on the network as a performance measurement.
route
Route (command) Manipulates network routing tables.
route is a command used to view and manipulate the TCP/IP routing table. Manual manipulation of the routing table is characteristic of static routing.
arp, Address Resolution Protocol, IP to MAC address
Address Resolution Protocol (arp) is a telecommunications protocol used for resolution of network layer addresses into link layer addresses, a critical function in multiple-access networks. ARP was defined by RFC 826 in 1982. It is Internet Standard STD 37. It is also the name of the program for manipulating these addresses in most operating systems.
ARP has been implemented in many combinations of network and overlaying internetwork technologies, such as IPv4, Chaosnet, DECnet and Xerox PARC Universal Packet (PUP) using IEEE 802 standards, FDDI, X.25, Frame Relay and Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM), IPv4 over IEEE 802.3 and IEEE 802.11 being the most common cases.
In Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) networks, the functionality of ARP is provided by the Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP).
ifconfig- display the link and address status of active interfaces
ip addr show- display the link and address status of active interfaces
route -n- display all the routing table in numerical addresses
ip route show- display all the routing table in numerical addresses
arp- display the current content of the ARP cache tables
ip neigh- display the current content of the ARP cache tables
plog- display ppp daemon log
ping yahoo.com- check the Internet connection to "yahoo.com"
whois yahoo.com- check who registered "yahoo.com" in the domains database
traceroute yahoo.com- trace the Internet connection to "yahoo.com"
tracepath yahoo.com- trace the Internet connection to "yahoo.com"
mtr yahoo.com- trace the Internet connection to "yahoo.com" (repeatedly)
dig [@dns-server.com] example.com [{a|mx|any}]- check DNS records of "example.com" by "dns-server.com" for a "a", "mx", or "any" record
iptables -L -n- check packet filter
netstat -a- find all open ports
netstat -l --inet- find listening ports
netstat -ln --tcp- find listening TCP ports (numeric)
dlint example.com- check DNS zone information of "example.com"
nslookup→ find the ip address of a domain name.netstat -rn=ip routhostname= display hostname- iwconfig – displays information from wireless
- telnet
- sudo iwlist scan – scan wireless networks
- sudo /etc/init.d/networking restart – reset the network
- (file) /etc/network/interfaces – manual configuration
- ifup interface – bring online interface
- ifdown interface – disable interface
using ufw
ufw is a simple command line to Linux's firewall features.
- ufw enable – turn on the firewall
- ufw disable – turn off the firewall
- ufw default allow – allow all connections by default
- ufw default deny – drop all connections by default
- ufw status – current rules and
- ufw allow port – to allow traffic on port
- ufw deny port – port block
- ufw deny from ip – ip block
short intro: Linux: What's Netfilter, iptables, Their Differences?
lsof -iLsofslurmiptraftrafshow
tctraffic control
Netlink «Netlink is a socket family used for IPC between the kernel and user space processes, as well as between user processes (e.g. UNIX sockets) or a mixture of both types. However, unlike INET sockets, it cannot traverse host boundaries, as it addresses processes by their (inherently local) PIDs.»
Netfilter «Netfilter is a set of hooks inside the Linux kernel that allows kernel modules to register callback functions with the network stack. A registered callback function is then called back for every packet that traverses the respective hook within the network stack.[1].»