Xah Talk Show 2024-10-27 Ep592, Wolfram Language, Advent of Code 2023, Day 14 Part 2, Take 3

Write Function to Detect Periodicity

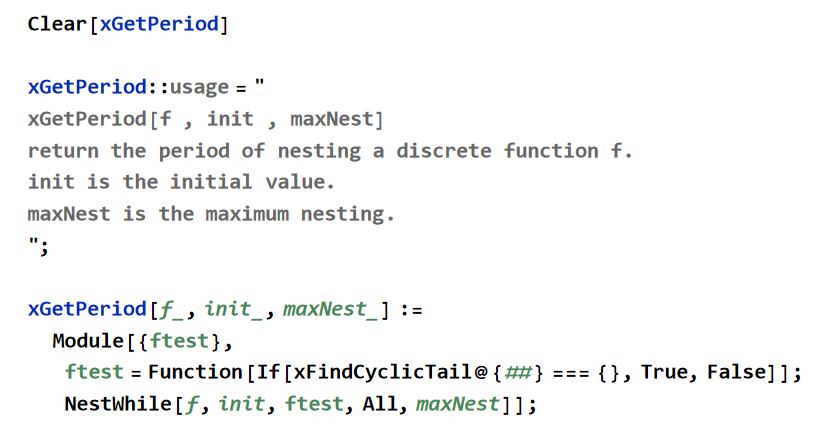
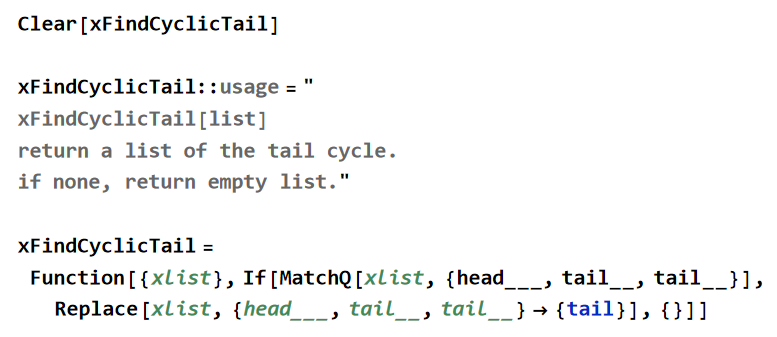
(* simple example of a discrete periodic function *) Clear[xmod5] xmod5[x_] := Mod[ x, 5 ]; Table[{x, xmod5[x]}, {x, 0, 20}] (* s------------------------------ *) (* the periodic of function is different from the period of nesting the function. for example xmod5[x_] := Mod[ x, 5 ] has period 5. but if you nest xmod5, then the period is 1. *) (* s------------------------------ *) (* what is period defined. it means, the sequence of output repeats. *) (* s------------------------------ *) (* is it possible for a discrete function to have a different nesting period for different init value. yes. not sure what's a simple example, but lots in dynamical systems butterfly effect *) (* s------------------------------ *) (* Hailstone function. If the number is even, divide it by two. If the number is odd, triple it and add one. this is a example, where the nesting period does not depends on init value. it's always 3. *) Clear[hailstone]; hailstone[x_] := If[ EvenQ[ x ], x/2, x 3 + 1]; NestList[ hailstone, 27 ] (* s------------------------------ *) Clear[xFindCyclicTail] xFindCyclicTail::usage = " xFindCyclicTail[list] return a list of the tail cycle. if none, return empty list." xFindCyclicTail = Function[{xlist}, If[ MatchQ[ xlist, {head___, tail__ , tail__ } ] , Replace[ xlist, {head___, tail__ , tail__ } -> {tail} ] , {}] ] xFindCyclicTail[{9,3,2,3,2}] (* s------------------------------ *) (* write a function to detect periodicy of nesting a given discrete function. algo: compute the function starting at init value. nest in, for n times. for each time you compute the function, save the value as a history list, and, compare, if current value is in history list. if the current output match a value in history, then, when you compute the next value, you need to check if it match the next value in history. do this check again, until, an output is the init matched value in history list. *) Clear[xGetPeriod] xGetPeriod::usage = " xGetPeriod[f , init , maxNest] return the period of nesting a discrete function f. init is the initial value. maxNest is the maximum nesting. "; xGetPeriod[f_ , init_ , maxNest_] := Module[ {ftest}, ftest = Function[ If[ xFindCyclicTail @ {##} === {} , True , False ] ] NestWhile[ f , init, ftest, All, maxNest ] ]; xGetPeriod[xmod5, 99, 1000] (* s------------------------------ *) (* given a list, determine if the tail of the list repeats, aka cycle. e.g. {5, 9, 3, 2, 9, 3, 2, 9} write a function. Algo: check if last 2 elements is same. If so, cycle is 1. Check if last 4 elements is a cycle, e.g. {a b a b} if so, cycle is 2. Check if last 6 elements is a cycle, e.g. {a b c a b c} if so, cycle is 3. This is 2*n and so on. Until 2*n is greater than length of list *)
(* code from ResourceFunction["FindNestPeriod"]; by Richard Phillips. accessed on 2024-10-26 *) FindNestPeriod[f_, init_, maxStepsToTry_ : 100000] := Block[{triedsteps = 0}, With[{pointoncycle = NestWhile[{triedsteps++; f[First[#]], f[f[Last[#]]]} &, {init, f[init]}, UnsameQ @@ # &, 1, maxStepsToTry]}, If[triedsteps == maxStepsToTry, Failure["NoRepeatFound", Association["MaxSteps" -> triedsteps]], Block[{cyclelength = 1}, NestWhile[(cyclelength++; f[#]) &, f[pointoncycle], # =!= pointoncycle &]; cyclelength]]]]
- Supercomputer
- Dynamical system
- Butterfly effect
- Collatz conjecture
Xah Talk Show, Advent of Code 2023, Day 14, Wolfram Language
- Xah Talk Show 2024-10-18 Ep588, Advent of Code 2023, Day 14, Wolfram Language
- Xah Talk Show 2024-10-22 Ep590, Advent of Code 2023, Day 14 Part 2, Wolfram Language
- Xah Talk Show 2024-10-26 Ep591, Wolfram Language, Advent of Code 2023, Day 14 Part 2, take 2
- Xah Talk Show 2024-10-27 Ep592, Wolfram Language, Advent of Code 2023, Day 14 Part 2, Take 3
- Xah Talk Show 2024-10-31 Ep595, Wolfram Language, Detect Nesting Function Periodicy, Advent of Code 2023, Day 14 Part 2, Take 4