Wolfram: Equality Test
SameQ[expr1, expr2]-
🔸 SHORT SYNTAX:
===return
Trueif two expressions are symbolically identical, elseFalse.{a,b,c} === {a,b,c} (* True *) {a,b,c} === {a,b,{c}} (* False *) 3 === 3 (* True *) 3 === 3.0 (* False *) Equal[expr1, expr2]-
🔸 SHORT SYNTAX:
==- return
Trueif two expressions are semantically equal. (e.g.3vs3.0) - return
Falseif two expressions are not semantically equal. - return whole expression as is, if semantic equality cannot be determined easily or WolframLang quirk.
3 == 3 (* True *) 3 == 3.0 (* True *) {3} == {3.0} (* True *) 🛑 WARNING:
Equaldoes not returnFalseeven for obvious cases such as{} == 2. It's designed that way because leaving the structure as is allows you to later replace parts of the expression such as byReplaceAlland then getTrueorFalse. If it becameFalseright away, the expression became inert.{} == 2 (* return expression as is. Version 13 *) (* using Reduce makes it true *) Reduce[ {} == 2 ] === True (* WARNING *) {{1}} == {2} (* return expression as is. Version 13 *) {{1.0}} == {2.0} (* return expression as is *) 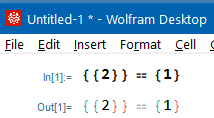
WolframLang equality issue 2022-09-18 - return
Inequality
UnsameQ-
🔸 SHORT SYNTAX:
=!=Same as
Not[SameQ[x, y]]. Unequal-
🔸 SHORT SYNTAX:
!=Same as
Not[Equal[x, y]].
🟢 TIP: What Function to Use for Equality Test
- Use
SameQwhen the expressions do not contain numbers with decimal point. It always returnTrueorFalse. - Use
Equalwhen you have numbers with decimal point.