Xah Talk Show 2025-12-27 Ep734 Wolfram Language, Advent of Code 2025, Day 5, Part 2 (failed)
Video Summary (Generated by AI, Edited by Human.)
This video, titled "Xah Ep734 Wolfram Language, Advent of Code 2025, Day 5, part 2 (failed)", features Xah Lee attempting to solve an Advent of Code problem (Day 5, Part 2) using Wolfram Language.
Here's a summary of the key points:
Introduction and Setup (0:00-1:05): Xah Lee welcomes viewers and introduces the Advent of Code 2025, Day 5, Part 2 problem he will be working on. He also briefly mentions his website, xahlee.info, which contains tutorials on Wolfram Language.
Wolfram Language Tutorial Resources (1:08-1:34): He highlights his comprehensive Wolfram Language tutorial on his website, covering basics, syntax, data structures, functions, variables, and loops. He also mentions that Wolfram Engine can be downloaded for free.
Introduction to Tools (1:47-4:03): Xah Lee introduces his coding environment, including the Ultimate Hacking Keyboard (UHK80), Emacs (text editor), and Sofy Keys (efficient keybinding system for Emacs). He also explains his use of the Dvorak keyboard layout and how the pink window displays his commands and keystrokes.
Problem Description: Advent of Code Day 5 Part 2 (4:06-8:04): Xah Lee explains the problem, which involves identifying "fresh ingredient IDs" from given ranges. Unlike Part 1, where the goal was to count numbers within a range, Part 2 requires finding the total count of distinct numbers across multiple, potentially overlapping, ranges. He goes through an example to illustrate the problem.
Naive Solution and Its Limitations (8:09-13:42): He describes a "naive" approach: generating a list of all numbers for each range, then performing a set union to find unique numbers, and finally counting the length. However, he demonstrates that this approach is not feasible due to the extremely large numbers involved (up to 221 terra, which is 10 followed by 12 zeros), leading to insufficient memory.
Digression: Keyboard Layouts and Ergonomics (13:39-26:04): A viewer asks about the difference between staggered and ortholinear (grid-aligned) keyboards. Xah Lee takes a significant digression to explain the history of keyboard staggering (due to mechanical typewriter mechanisms 200 years ago) and contrasts it with modern ortholinear designs. He discusses various ergonomic keyboard features like split designs, tenting, key switches, and keycap design. He concludes that while ortholinear is theoretically better, the practical difference for experienced typists isn't substantial, and habit often dictates user preference.
Proposed Algorithm for Overlapping Ranges (26:11-39:15): Returning to the coding problem, Xah Lee proposes a more efficient algorithm to handle the large number ranges. The steps include:
Sorting: Sort the ranges by their minimum (first) number (26:52, 36:11).
Duplicate Removal: If two neighboring ranges are identical, remove one (37:15, 38:28).
Overlapping Ranges: Identify neighboring ranges that overlap. If range A overlaps with range B, reduce the max of range A to be one less than the min of range B (33:17, 34:02).
Wolfram Language Implementation (Attempt) (41:07-1:19:40): Xah Lee begins implementing his proposed algorithm in Wolfram Language. He goes through steps of processing the input to create a list of ranges, sorting them, and attempting to apply the logic for merging overlapping ranges. He encounters difficulties with the Flatten function and debugging the code, leading to an incorrect result (26 instead of the expected 14 from the example problem). The video ends with him debugging the solution.
keyboard links
- Why Are Keyboard Keys Not Aligned Vertically?
- Keyboard Design 🔧
- Ultimate Hacking Keyboard 80 (UHK 80)
- Ergonomic Keyboard Layouts
- Royal Bar-Lock Typewriter
- Computer Keyboards ⌨
- Keyboard History ⌨
- Ergonomic Keyboard Reviews
- X-Bows Knight Keyboard
- Apple Laptop Keyboards ⌨
- Thinkpad Keyboard
- Laptop Keyboards
- Apple iBook G4 (year 2003)
- MacBook Air M1 (2021)
- MacBook Pro 16-inch, 2019
- Invac PK-200 keyboard. 1966

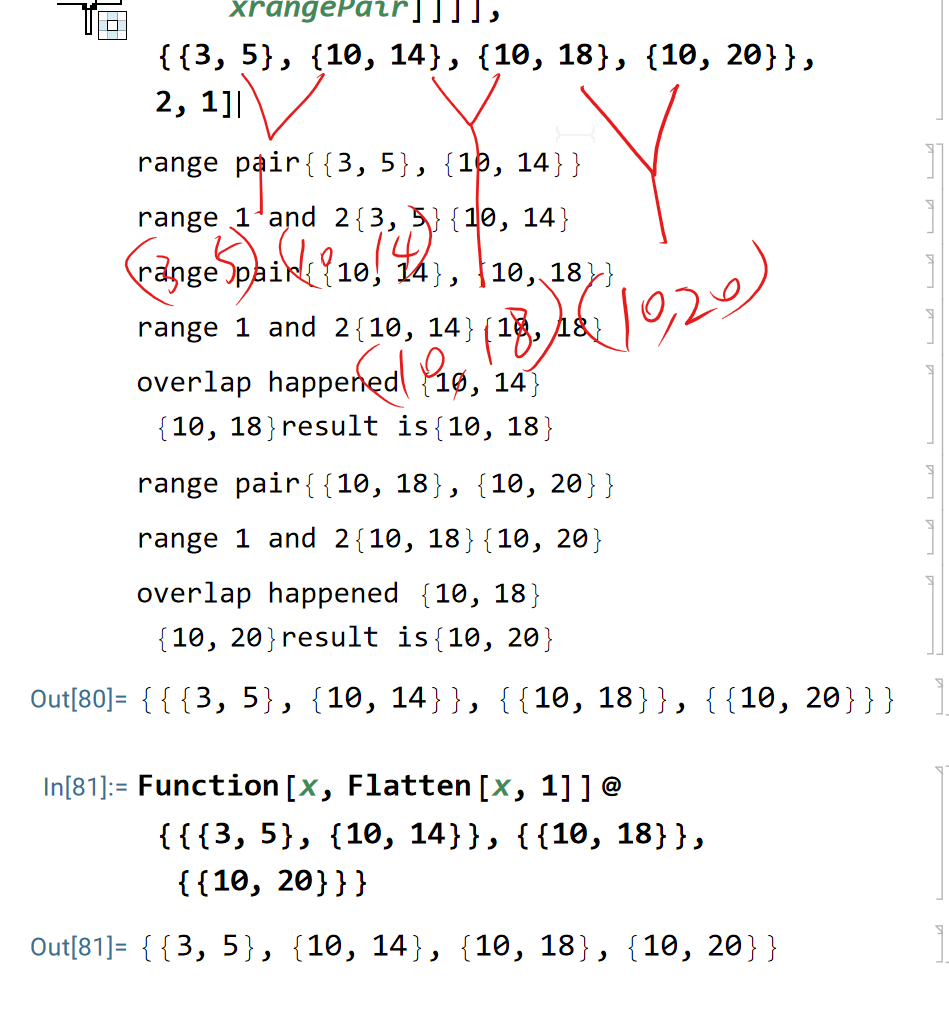
- The fatal flow in my algorithm.
- Else this algo is superb, because it is doing parallel computing.
- to still use this algo, it needs to partition but no overlap, but you need to shift the position of the gabs. that'd be ugly.
- alternative is to use recursion, aka Nest, and deal with one pair of ranges at the time, and split them into head and tail, where heads are done, tail are to be processed.
problem description.
given a list of ranges, e.g.
- 3-5
- 10-14
- 16-20
- 12-18
find how many total distinct numbers are in them.
naive solution
- the naive way to solve this problem, is just to generate a list of numbers for each range.
- then, you do a set union of all the lists.
- then, you just get the length.
- but, the naive solution won't work,
- because the number range has too many numbers to fit into memory.
better solution. algo description
- now, here's a better solution.
- given a list of ranges,
- 3-5
- 10-14
- 16-20
- 12-18
first we sort them, by their min.
- 3-5
- 10-14
- 12-18
- 16-20
- then, if it so happens that 2 neighboring rages are identical, remove one of them. (remove all such duplicate ranges)
- then, you find neighboring ranges that overlap.
- to determine overlap, check the max of 1s
- two ranges overlap, if the max of first range is greater or equal to the min of the second range.
- when you find 2 ranges that overlap, e.g.
- 12-18
- 16-20
- you reduce the max of the first range by the min of the second range minus 1.
- e.g.
- 12-18
- becomes
- 12-15
- (because 16 -1)
solution
xrangeList = {{3, 5}, {10, 14}, {16, 20}, {12, 18}} xsortedRanges = SortBy[xrangeList , First] (* {{3, 5}, {10, 14}, {12, 18}, {16, 20}} *) DeleteDuplicates[ {{3, 5}, {12, 18}, {10, 14}, {12, 18}, {16, 20}}] (* {{3, 5}, {12, 18}, {10, 14}, {16, 20}} *) xsortedRanges = DeleteDuplicates[ xsortedRanges ] Partition[{a , b , c , d , e}, 2, 1] (* {{a, b}, {b, c}, {c, d}, {d, e}} *) (* each of the a b c etc is a range. e.g. {a , b} are neighboring ranges. *) Map[ ff , {{a, b}, {b, c}, {c, d}, {d, e}}] (* {ff[{a, b}], ff[{b, c}], ff[{c, d}], ff[{d, e}]} *) (* here's what ff will do. *) Function[xrangePair, With[{xrange1 = First@x, xrange2 = Last@x}, If[Last@xrange1 >= First@xrange2, {First@xrange1, Last@xrange2}, xrangePair]]]
xinput = "3-5 10-14 16-20 12-18 1 5 8 11 17 32"; xrangeList = ToExpression @ StringSplit[ StringSplit[ StringSplit[xinput , "\n\n"][[1]], "\n"] , "-"] (* {{3, 5}, {10, 14}, {16, 20}, {12, 18}} *) xrangeList = DeleteDuplicates @ SortBy[xrangeList , First] Function[ff, FixedPoint[ ff, xrangeList]] @ Function[xrangeList, Function[x, Flatten[x,1]] @ BlockMap[ Function[xrangePair, With[{xrange1 = First@xrangePair, xrange2 = Last@xrangePair}, If[ xrange1 === xrange2, xrange1, If[Last@xrange1 >= First@xrange2, {{First@xrange1, Last@xrange2}}, xrangePair] ] ]], xrangeList, 2] ] BlockMap[ff,{aa,bb,cc,dd,ee},2] (* {ff[{aa, bb}], ff[{cc, dd}]} *) (* new algo. a function ff, that takes a list of 2 things. {headList, tailList} of is form ff[{headList, tailList}] headList is a list of ranges that do not overlap. initially, it is empty. tailList is a list of ranges to be processed. the function returns a new {headList, tailList}. by comparing the last time in headList with the first item in tailList. if they do not overlap, move the first item in tailList to headList. if they do overlap, merge it, put result in head list. *) (* s------------------------------ *) (* fatal flow using BlockMap. instead, just map 2 ranges, don't over lap them. then repeat. *) (* s------------------------------ *) Function[xrangeList, Function[x, Partition[Flatten[x], 2]]@ BlockMap[ff, xrangeList, 2, 1]]@{{3, 5}, {10, 14}, {10, 18}, {10, 20}} Partition[Flatten[BlockMap[ff, {{3, 5}, {10, 14}, {10, 18}, {10, 20}}, 2, 1]], 2] BlockMap[ff, {{3, 5}, {10, 14}, {10, 18}, {10, 20}}, 2, 1] (* s------------------------------ *) FixedPoint[Function[xrangePairList, Function[x, Partition[Flatten[x],2]] @ Map[ Function[xrangePair, With[{xrange1 = First@xrangePair, xrange2 = Last@xrangePair}, If[Last@xrange1 >= First@xrange2, {First@xrange1, Last@xrange2}, xrangePair]]] , xrangePairList ] ], xrangePairList] (* s------------------------------ *) (* Partition[DeleteDuplicates @ SortBy[ {{3, 5}, {10, 14}, {16, 20}, {12, 18}} , First] , 2, 1] *) (* {{{3, 5}, {10, 14}}, {{10, 14}, {12, 18}}, {{12, 18}, {16, 20}}} *) (* Function[x, Partition[Flatten[x],2]] @ {{{3, 5}, {10, 14}}, {10, 18}, {12, 20}} *) (* {{3, 5}, {10, 14}, {10, 18}, {12, 20}} *)
Advent of Code 2025
- Xah Talk Show 2025-12-08 Ep720 Wolfram Language, Advent of Code 2025, Day 1
- Xah Talk Show 2025-12-09 Ep721 Wolfram Language, Advent of Code 2025, Day 1, Part 2
- Xah Talk Show 2025-12-11 Ep723 Wolfram Language, Advent of Code 2025, Day 1, Part 2, take 2
- Xah Talk Show 2025-12-12 Ep724 Wolfram Language, Advent of Code 2025, Day 2
- Xah Talk Show 2025-12-15 Ep725 Wolfram Language, Advent of Code 2025, Day 2, Part 2
- Xah Talk Show 2025-12-17 Ep726 Wolfram Language, Advent of Code 2025, Day 3 (aborted)
- Xah Talk Show 2025-12-18 Ep727 Wolfram Language, Advent of Code 2025, Day 3, take 2
- Xah Talk Show 2025-12-19 Ep728 Wolfram Language, Advent of Code 2025, Day 3, Part 2 (failed)
- Xah Talk Show 2025-12-20 Ep729 Wolfram Language, Advent of Code 2025, Day 4
- Xah Talk Show 2025-12-21 Ep730 Wolfram Language, Advent of Code 2025, Day 4, take 2
- Xah Talk Show 2025-12-22 Ep731 Wolfram Language, Advent of Code 2025, Day 4, Part 2. Wolfram vs SageMath
- Xah Talk Show 2025-12-23 Ep732 Wolfram Language, Advent of Code 2025, Day 4, Part 2. take 2
- Xah Talk Show 2025-12-26 Ep733 Wolfram Language, Advent of Code 2025, Day 5
- Xah Talk Show 2025-12-27 Ep734 Wolfram Language, Advent of Code 2025, Day 5, Part 2 (failed)
- Xah Talk Show 2026-01-02 Ep736 Wolfram Language, Advent of Code 2025, Day 6
- Xah Talk Show 2026-01-05 Ep738 Wolfram Language, Advent of Code 2025, Day 6, Part 2
- Xah Talk Show 2026-01-09 Ep741 Wolfram Language, Advent of Code 2025, Day 7
- Xah Talk Show 2026-01-13 Ep744 Wolfram Language, Advent of Code 2025, Day 7, part 2
- Xah Talk Show 2026-01-24 Ep749 Wolfram Language, Advent of Code 2025, Day 8