PowerShell: Show File Attributes
Meaning of Mode Column Letters in dir Output
Common attributes are displayed in the first column of output of Get-ChildItem
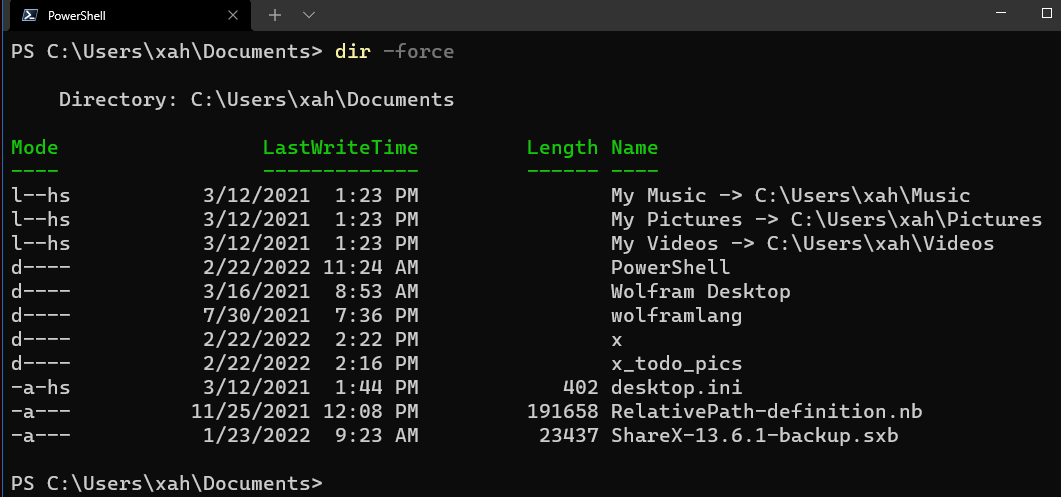
Meaning of the mode letters:
l(link. Link points to another file) ord(directory).a(archive) → marked for backup. (file been modified since last backup)r(read-only)h(hidden)s(system)
Show All Attributes of a File or Dir
# list all attributes of a file or dir Get-ItemProperty "~/Downloads/" -Name Attributes # Attributes : ReadOnly, Directory # PSPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\FileSystem::C:\Users\xah\Downloads\ # PSParentPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\FileSystem::C:\Users\xah # PSChildName : Downloads # PSDrive : C # PSProvider : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\FileSystem

PowerShell. File Properties, Attributes, Permission
- PowerShell: File Properties
- PowerShell: File Attributes
- PowerShell: List All Possible File Attribute Values
- PowerShell: Show File Attributes
- PowerShell: Show Hidden Files
- PowerShell: List Files with Specific Attribute
- PowerShell: Set a File's Attributes
- PowerShell: Set File Read Only Attribute
- PowerShell: File Attributes Object Type
- PowerShell: Change File Owner Perm (ACL)