Emacs: Byte Compile Elisp Files
What is Byte Compiled File
Emacs lisp files can be byte compiled.
- Any emacs lisp file can be byte compiled into a file.
- Any emacs lisp expression can be byte compiled.
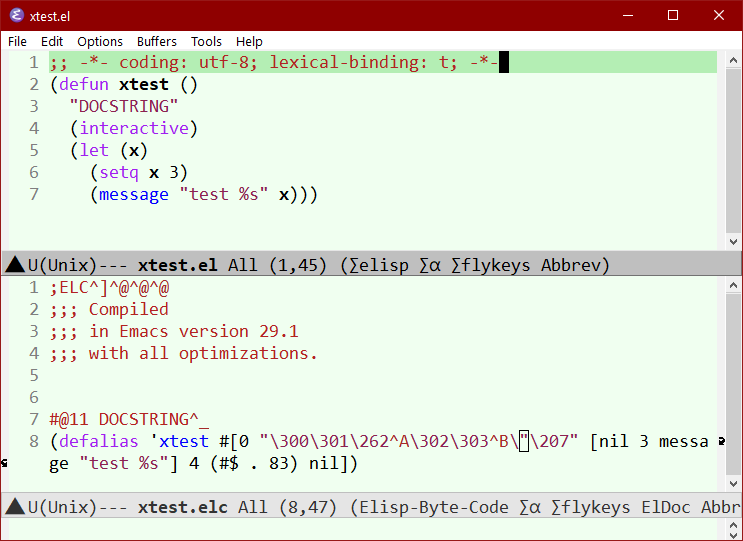
- Byte compiled elisp file has file name extension
.elc - Normal elisp file is
.el
Advantage of Byte Compiled Elisp File
- Byte compiled elisp files load faster.
- Byte compiled elisp functions also run faster. (by a simple test of a loop 50 million times, it is about 8 times faster.)
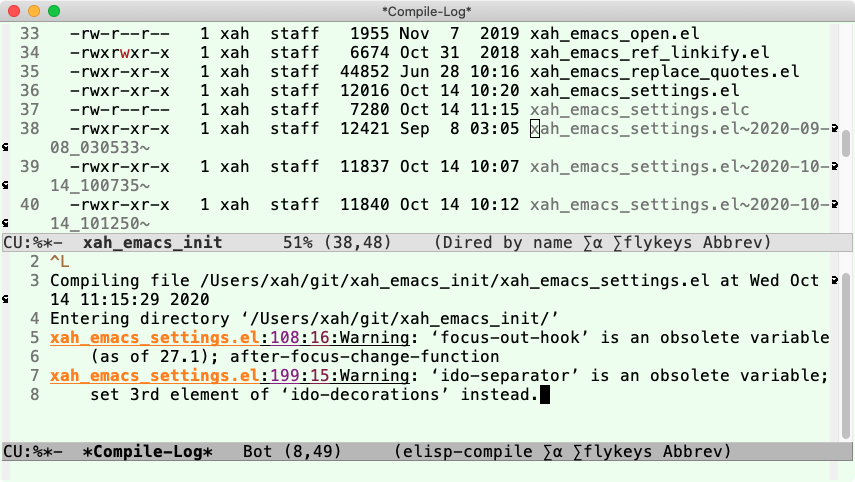
- Byte compiling will often tell you errors or warning in your elisp code that you normally wouldn't know.
As of today (2023-08-23), for init files and light-weight packages, byte compile don't make any noticeable speed difference.
How to Byte Compile Emacs Lisp File
There are several ways to byte compile elisp files. The simplest and most useful are:
- Alt+x
byte-compile-file - Compile a single file. It'll ask for a file name.
- Alt+x
dired-do-byte-compile【B】 - Compile all marked files in dired.
- Alt+x
byte-recompile-directory - Batch compile all elisp files in current dir and subdirectory.
Loading Byte Compiled File
When emacs loads emacs lisp files,
normally it will load the byte compiled version if exist.
Typically by looking for the file name with the
.elc
suffix.
The most fundamental loading file mechanism in emacs is the function
load.
Your init file, if you are using load,
do not add the file name extension such as
.el
or
.elc.
This way, emacs will automatically load the byte compiled version
when exist.
;; load elisp file, use byte compiled version (.elc) if exist (load "my_emacs_keybinding") ;; no file name extension here
Recompile When Upgrade
you should recompile your elisp files when:
- upgrade to a new emcas version
- upgrade packages
- moving byte compiled elisp directory from one machine to another
because often, emacs has some incompatible elisp changes, and big packages may fail without recompile.
Reference
2011-07-15 thanks to Adolfo Benedetti https://twitter.com/adben .