Wolfram: Surface Color
xtodo work in progressHow Surface is Colored
In 3D graphics, how surface is colored is determined by many things.
It depends on:
- Intrinsic color of the surface. Think of it as the property of the material.
- Lighting.
Intrinsic color
Intrinsic color can be:
- Diffuse color.
- Glowing color.
- Specularity (like shiny metal).
- Transparency degree. (like glass)
- Lighting spec can also be attached to surface. (this seems odd)
Intrinsic color can also change on the surface. e.g. change by height of a function.
Global Lighting
Lighting interacts with surface color.
Types of Intrinsic Color
xtodoPlotStyle
For plotting functions, color of surface is added by using option PlotStyle.
ColorFunction
Add different color to different parts of surface by a function.
Color Spec for 3D Graphics
Opacity
Glow
Glow-
- Make the surface glow.
- When there is no light source, glow surface still can be seen.
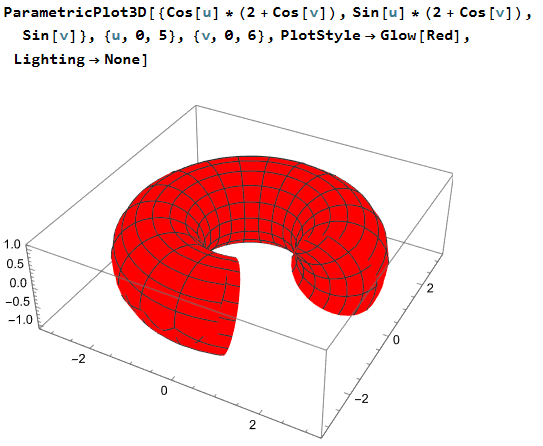
Wolfram Glow 2025-06-20 18c87 ParametricPlot3D[ {Cos[u]*(2 + Cos[v]), Sin[u]*(2 + Cos[v]), Sin[v]} , {u, 0, 5}, {v, 0, 6}, SphericalRegion -> True, PlotStyle -> Glow[Red], Lighting -> None ] 🟢 TIP: If you want to color a surface purely by its height or curvature or other variable, without any lighting effect,
- Set color to be glow.
- Set color to be black.
- Set specularity to be none.
- Turn global lighting off. E.g.
Lighting -> None
Directive[Glow[color], Black, Specularity[0]]
Specularity
Specularity-
- Make surface shiny, reflective, like a polished metal.
- Strong interaction with
Lighting.