Linux: Record Terminal Session, Log Shell Output
If you do a lot sys admin work, or you want a record of your shell session, you can log it to a file. There are several ways to do this.
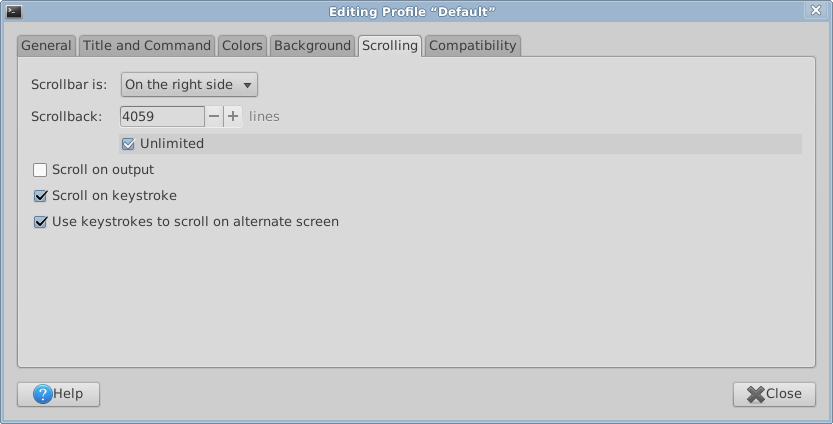
Set Terminal Scrollback to Unlimited, Copy and Save
One way is set your terminal to unlimited scrollback, then, just select all, copy, then paste and save in a editor.
To set unlimited scrollback, in gnome-terminal, it's under menu [Edit ▸ Profile Preferences ▸ Scrolling] tab. If your terminal doesn't have unlimited/infinite option, just use a big number.
Then, when you need to save session, just pull menu [Edit ▸ Select All] , then menu [Edit ▸ Copy] , then paste it in a editor.
This is a nice solution, but the problem is, in some dumb terminal such as Linux: Virtual Terminal , there is no menu or copy and paste.
Using “script” Command to Log Session
Start logging like this script ~/session.log.
Stop logging by exit.
Problem with this solution is:
- You have to remember to start logging.
- The saved log isn't pretty. It contains lots control sequences, it also contain man page. For example, you started to view a man page, and you page up and down several times, all the screen text are logged.
- The command
exitto stop logging is a problem, because sometimes you don't remember if you started “script” or not, and if you typeexit, it exits your shell, and closes the terminal window, and you lose all data. (whether exit shell or Ctrl+d closes the window/tab depends on your terminal app.)
Using Shell inside Emacs
Best is to use shell inside emacs. That way, you don't have to worry whether you forgot to start to log it. Just save it to a file anytime.
Start emacs, then call shell to start shell. To save, call write-file.
For a detailed tutorial, see: Emacs Shell Tutorial (Bash, cmd.exe, PowerShell)
.
Add Timestamp to Your Shell Prompt
When logging, it's good to have timestamp. see: