JS: Object Literal Expression
Object Literal Expression Syntax
The most useful and simple way to create a data object is using the literal expression.
{k1:v1, k2:v2, etc }-
Return a new object with properties key k1 value v1, etc.
Property Key must be string or symbol, else, they are converted to string.
console.log({ aa: 7, bb: 8 }); // { aa: 7, bb: 8 }
Trailing Comma is Ignored
// single trailing comma is ignored // deno-fmt-ignore const x = { aa: 7, bb: 8, }; console.log(x); // { aa: 7, bb: 8 }
Repeated Comma is Syntax Error
// more than one trailing comma is error // deno-fmt-ignore const x = { aa: 7, bb: 8,, }; // error: The module's source code could not be parsed:
// cannot have repeated comma // deno-fmt-ignore const x = { aa: 7,, bb: 8 }; // error: The module's source code could not be parsed:
🛑 WARNING: confusing error with code block syntax
if you type
{ a: 7, b: 8 }
you may get a syntax error about unexpected token colon.
SyntaxError: Unexpected token :
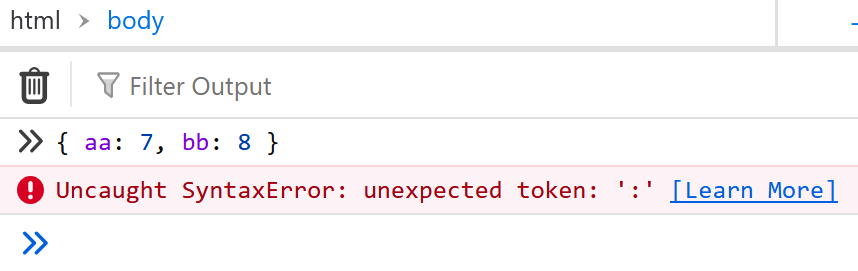
That is because JavaScript confused object literal with statement block syntax. Due to bad design of JavaScript.
solution is to add a paren:
({ a: 7, b: 8 })
Computed Property Key
(new in ECMAScript 2015)
If property key is enclosed by square bracket [key], the key is evaluated as expression.
obj = {[expression]:value}
- This is useful when you want a variable's value to be the property key.
- This syntax is necessary for property key that is Symbol.
// object literal expression, with a computed key name from a variable const xx = "cc"; const jj = { [xx]: 3 }; console.log(jj); // { cc: 3 }
// create a key named ab, by eval an expression const jj = { ["a" + "b"]: 4 }; console.log(jj.ab); // 4
Function as Property Value
Example of a property value that is a function.
// object with methods const jj = { // define property as a function ff: function (x) { return x + 1; }, // arrow function syntax gg: ((x) => (x + 1)), // data property pp: 4, }; // call the function ff console.log(jj.ff(3)); // 4 // call the function gg console.log(jj.gg(3)); // 4
Method Syntax Shorthand
(new in ECMAScript 2015)
If the property value is a function definition by the keyword function, it has a shortcut syntax.
obj = { fname: function (args) {body} }
can be written as:
obj = { fname(args) {body} }
const jj = { ff(x) { return x + 1; }, }; console.log(jj.ff(2)); // 3
Parent of Object Literal Expression
The parent of object created using Object Literal Expression is Object.prototype. 〔see JS: Prototype and Inheritance〕
JavaScript. Object and Inheritance
- JS: Object (basics)
- JS: Object Overview
- JS: Object Type
- JS: Test is Object Type 📜
- JS: Find Object's sub-type
- JS: Prototype and Inheritance
- JS: Prototype Chain
- JS: Object.prototype.isPrototypeOf
- JS: Get Set Prototype
- JS: Show Prototype Chain 📜
- JS: Prototype Tree
- JS: Dot Notation and Prototype Chain
- JS: Create Object
- JS: Object Literal Expression
- JS: Object.create
- JS: Object Literal Expression vs Object.Create
- JS: Create Object with Parent X
- JS: Prevent Adding Property
- JS: Deep Copy Array or Object 📜
- JS: Test Equality of Array and Object by Content 📜
- JS: Add Method to Prototype
- JS: Object (class)
- JS: Object Constructor
- JS: Object.prototype