Sine Curve
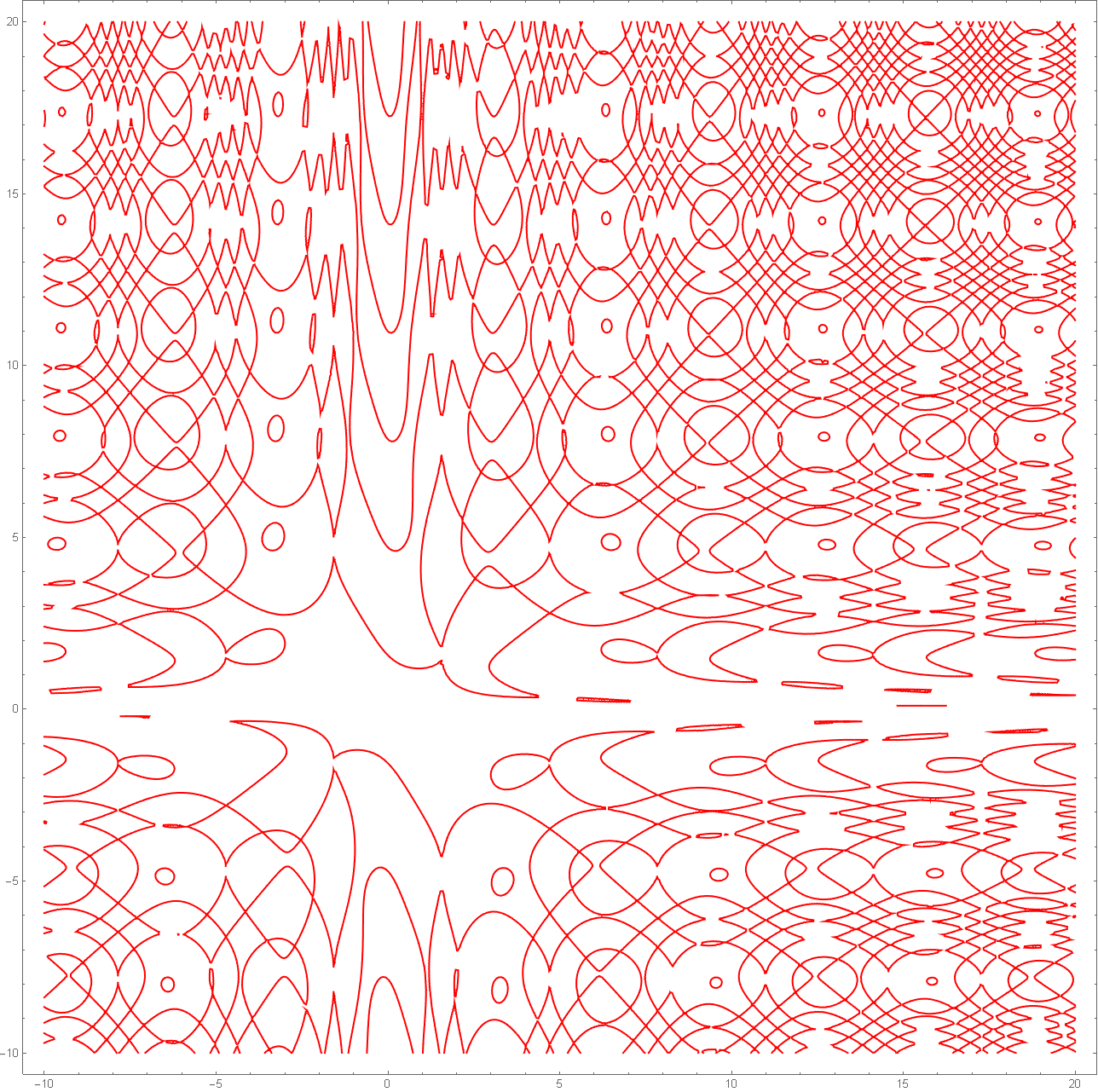
ContourPlot[ Sin[x*Sin[y]] - Cos[y*Cos[x]] == 0, {x, -10, 20}, {y, -10, 20}, PlotPoints -> 50, ColorFunction -> Hue]
History
All trignometric functions sine, cosine, tangent, secant, cosecant, cotangent can all be simply defined in terms of a single function sine. Sine, as associated with trigonometry, began in early civilization as a very important measuring science. When the function concept and calculus and analytic geometry were introduced in about 1700, sine became a function and has little to do with triangles. The sine function appears unexpectedly throughout analysis, because in essence it captures the idea of a wave, a fundamental concept in physics.
From Robert Yates:
Trigonometry seems to have been developed, with certain traces of Indian influence, first by the Arabs about 800 as a aid to the solution of astronomical problems. From them the knowledge probably passed to the Greeks. Johann Müller (c.1464) wrote the first treatise: De triangulis omnimodis; this was followed closely by others.
Description
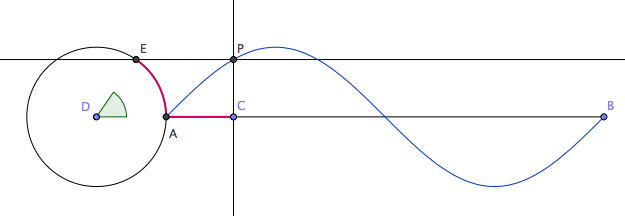
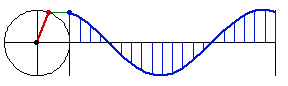
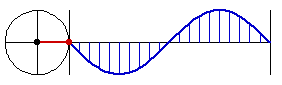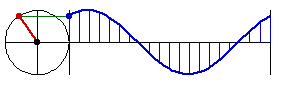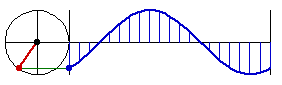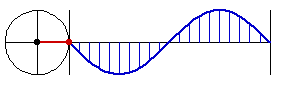
Sine curve is the curve of the sine function. It is also known as sinusoid. Sine is sometimes called circular function because the essential feature of the sine function can be thought of as a point moving around a circle in constant speed, and the value of sine being the height of the point.
Step by step description:
- Let A be a point on origin.
- Let C be a point on the positive x-axes.
- Let D be a point on (-1,0).
- The sine function at Distance[A,C] is the height of E, where E is a point such that ArcLength[A,D,E] == Distance[A,C].
Formula
In the formula y == a*Sin[x/p+s], a is the amplitude, p the period, and s the phase shift.
Trig Functions In Terms of Sine
All trig functions is defined in terms of sine.
| Sin[θ] | Csc[θ]:=1/Sin[θ] |
| Cos[θ]:=Sin[θ+Pi/2] | Sec[θ]:=1/Cos[θ] |
| Tan[θ]:=Sin[θ]/Cos[θ] | Cot[θ]:=1/Tan[θ] |
If a right triangle is placed in a standard position (That is: in the Cartesian coordinate system such that it lies in the first quadrant, and the right angle vertex lies on the x-axes, and the hypotenuse touches the origin), and if r denote (the length of) the hypotenuse, x the bottom side, y the vertical side, θ the angle of x and r, then we have the following formulas:
| Sin[θ] == y/r |
| Cos[θ] == x/r |
| Tan[θ] == y/x |
Properties
Basic Trig Functions
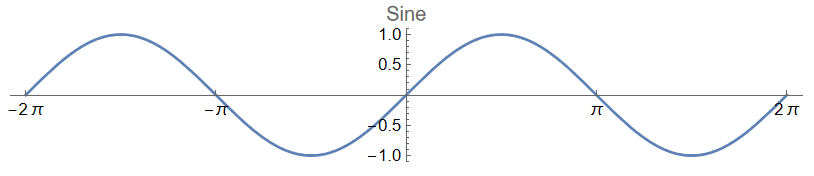
Plot[Sin[x], {x, -2 Pi, 2 Pi}, AspectRatio -> Automatic, PlotLabel -> "Sine", Ticks -> {Range[-2 Pi, 2 Pi, Pi], Automatic}]
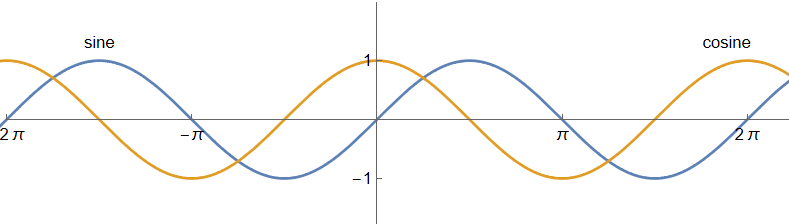
Plot[{ Sin[x], Cos[x] }, {x, -8, 8}, AspectRatio -> Automatic, PlotRange -> {{-2 Pi, 2 Pi}, {-2, 2}}, Ticks -> {Range[-4 Pi, 4 Pi, Pi], {-1,1}}, PlotLabels -> { Placed["sine", Above ], Placed["cosine", Above ] } ]
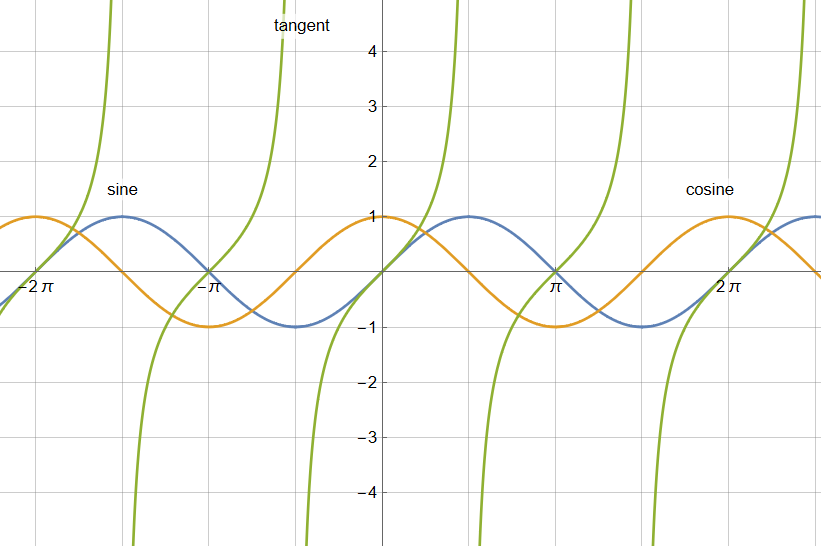
Plot[{ Sin[x], Cos[x], Tan[x] }, {x, -8, 8}, AspectRatio -> Automatic, PlotRange -> {{-2 Pi, 2 Pi}, {-4, 4}}, Ticks -> {Range[-4 Pi, 4 Pi, Pi], Range[-4,4] }, GridLines -> {Range[-4 Pi, 4 Pi, Pi/2], Range[-4,4]}, PlotLabels -> { Placed["sine", Above ], Placed["cosine", Above ], Placed["tangent", Above ] } ]
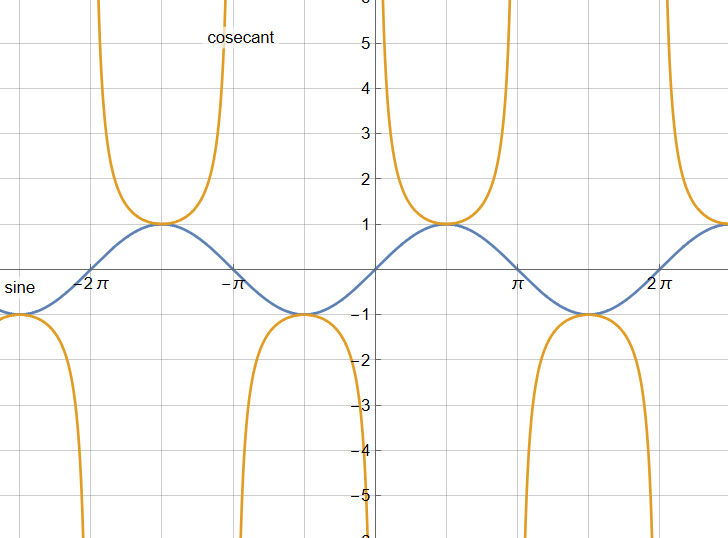
Plot[{ Sin[x], Csc[x] }, {x, -9,9}, AspectRatio -> Automatic, PlotRange -> {{-3 Pi, 3 Pi}, {-6, 6}}, Ticks -> {Range[-4 Pi, 4 Pi, Pi], Range[-6,6] }, GridLines -> {Range[-4 Pi, 4 Pi, Pi/2], Range[-6,6]}, PlotLabels -> { Placed["sine", Bottom ], Placed["cosecant", Above ] } ]
Helix Projection
Development Of Cut Cylinder
Sine curve is the development of a obliquely cut right circular cylinder. (the edge of the cylinder rolled out is a sinusoid). cylinder_develop.nb
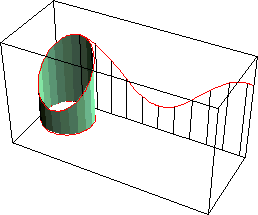
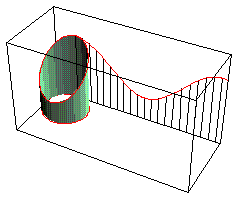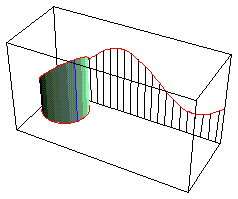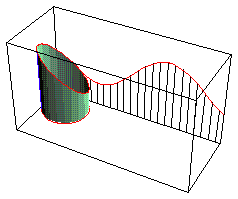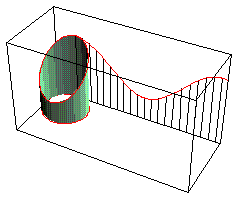
Wavy Surface

Sin[x] Sin[y]
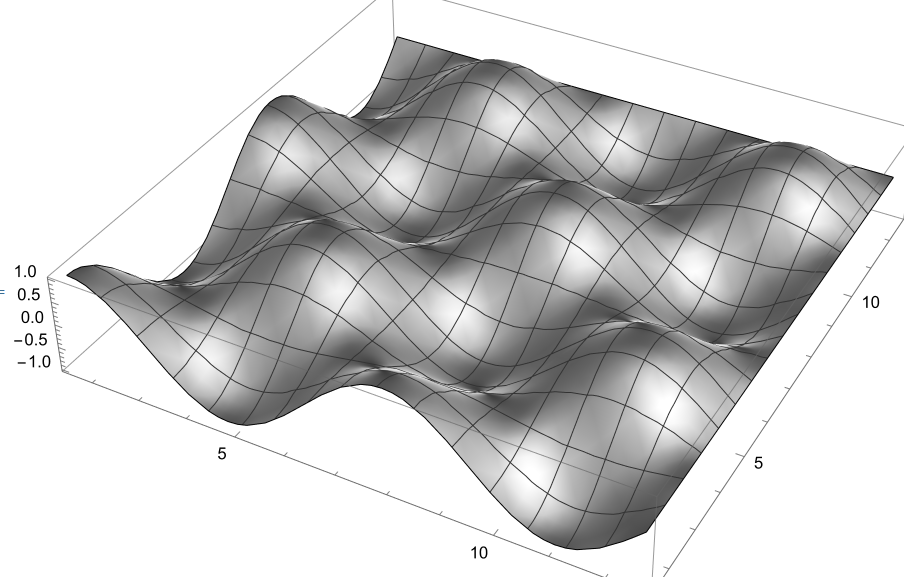
Plot3D[Sin[x]*Sin[y], {x, Pi/2, 4 Pi}, {y, Pi/2, 4 Pi}, BoxRatios -> Automatic, PlotStyle -> { MaterialShading["Silver"], Lighting -> "ThreePoint"}]
Math Art, Borg Cube
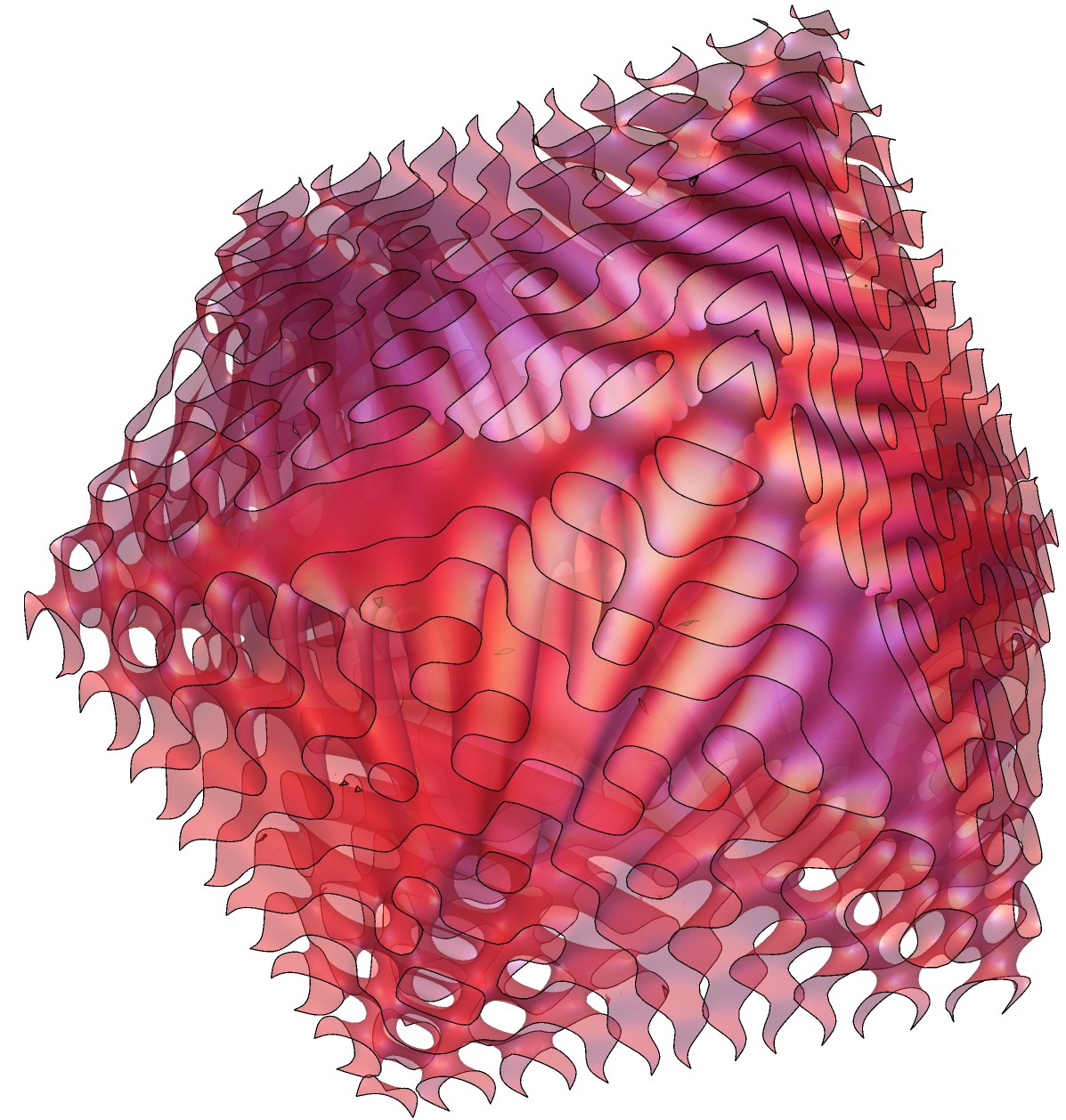
max = 5; ContourPlot3D[ Sin[x*y] + Sin[y*z] + Sin[z*x] == 0, {x, -max, max}, {y, -max, max}, {z, -max, max}, Boxed -> False, Axes -> False, Mesh -> None, ContourStyle -> Directive[RandomColor[], Opacity[0.5], Specularity[ 1, 20]]]